Written by Chris Hellmund (Senior Medical Writer) and Neil Webb (Head of Systematic Review)
A poster on this topic was presented at ISPOR Europe 2019. This blog post provides an overview of our findings.The abstract is available here.
In previous blog posts, we explored the origins of NICE’s Highly Specialised Technologies (HST) process and compared it with the Single Technology Assessment (STA) process.
In this blog, we review the first 10 HST appraisals and identify key issues raised by the Evidence Review Groups (ERGs).
The indications evaluated under the HST process are often associated with unavoidable limitations, such as small trial sample sizes, and limited quality of life and natural history data. However, identification of avoidable issues would enable us to develop recommendations for manufacturers completing future submissions.
Evidence challenges – SLR
Key issues in the reporting of SLRs were generally avoidable. In some submissions, search strategies were not comprehensive, for example because no proper attempt had been made to search for comparators, and not all terms and synonyms for the intervention had been included. Some submissions lacked transparency in reporting, and others failed to present the flow of studies through the SLR in a consistent and logical manner.
| Recommendations – systematic literature reviews
SLR strategies should be comprehensive, and SLRs should be reported in a fully transparent manner, allowing the methods to be reproduced. |
Evidence challenges – clinical evidence
Some criticisms of the clinical evidence presented may be considered unavoidable in the context of HSTs. For example, some trials were open label or lacked comparator arms. For novel technologies with innovative modes of action it may be neither possible nor ethical to use a placebo, and comparators may not exist. Additional unavoidable issues included lack of clarity about clinical relevance thresholds – if novel endpoints are used, established thresholds may not exist.
Potentially avoidable issues identified included statistical analyses being conducted differently for different trial outcomes, and inappropriate comparison of trial results with historical control data. Naïve comparisons with historical data were criticised due to the evolution of standard of care over time, and differences in inclusion criteria between studies.
Recommendations – clinical evidence
|
Evidence challenges – economic evidence
In 3/10 submissions the approach to generating utility values raised concerns. In one submission these related to the use of clinical experts rather than patients (as per the NICE reference case) for deriving utility values. In another, the ERG had concerns about the specification of a statistical model which was fitted to EQ-5D-5L data in the pivotal clinical trial. The model permitted impossible values (i.e. utility values above 1), and the ERG believed that it didn’t properly take into account the distribution of the underlying data. In the same submission, the ERG also had concerns about the assumption that patients in the best supportive care arm experienced considerable reductions in health related quality of life.
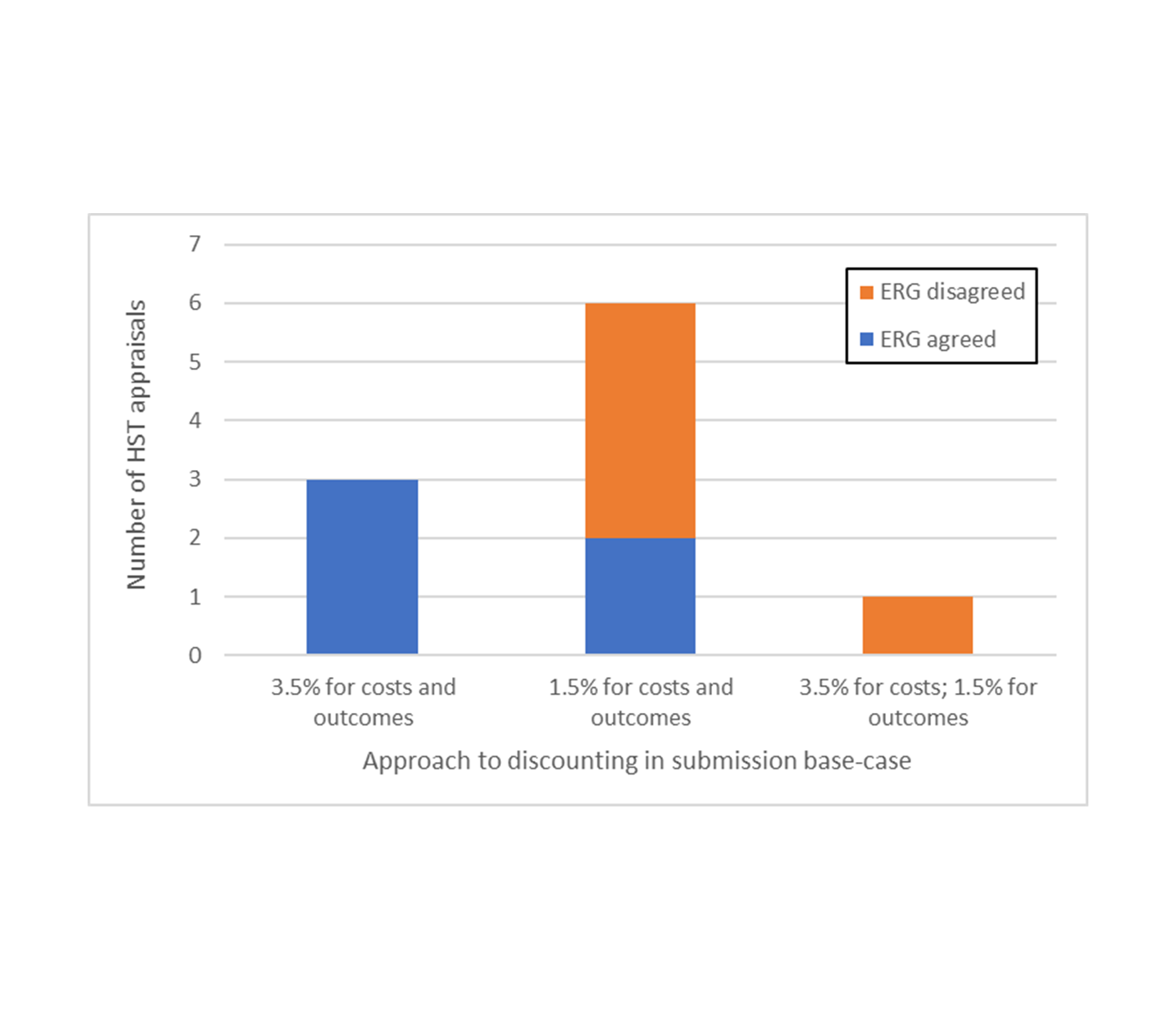
Given the potential for more frequent use of the 1.5% discount rate in HST submissions, it was of interest to assess how frequently ERGs accepted this approach. In line with the NICE Guide to the Methods of Technology Appraisal, interim HST guidance states that discount rates of 1.5% may be used if:
- treatment restores people to full or near full health when they would otherwise die or have a very severely impaired life, and this is sustained over a very long period (normally at least 30 years); and
- the introduction of the technology does not commit the NHS to significant irrecoverable costs [1].
Most submissions (6/10) used this 1.5% discount rate in the company base-case, with the remainder either using a 3.5% rate (3/10) or differential discounting of 3.5% for costs and 1.5% for outcomes (1/10).
The ERG agreed with the use of the 3.5% rate. However, in 4/6 cases where a 1.5% rate was used, the ERG felt the conditions for use of the lower discount rate had not been met and/or the ERG’s interpretation of NICE guidance was that the 1.5% rate should be presented as a scenario only, highlighting ambiguity in the interim HST guidance.
The use of differential discounting was rejected by the ERG in the one submission where it was used; the ERG stated that it is not considered appropriate, and both discount rates were set to 3.5%.
Figure 1: Approach to discounting across appraisals
Recommendations – economic evidence
|
Conclusions
By identifying key issues raised by ERGs and developing recommendations to mitigate these risks in future submissions, we hope that these findings can be of use to manufacturers making future HST submissions to NICE.